Are Password Managers Safe To Use?
Indeed, the safety of password managers is not only widely endorsed by cybersecurity experts, but it’s a stance we firmly support as well.
With sophisticated encryption at their core, password managers shield your credentials from potential breaches that could otherwise leave your passwords vulnerable, which is why you need a password manager.
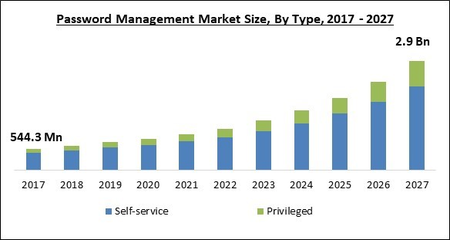
Source:https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5553149/global-password-management-market-by-type-by
“The Global Password Management Market size is expected to reach $2.9 billion by 2027, rising at a market growth of 20.7% CAGR during the forecast period.”
Despite occasional reports highlighting vulnerabilities, it’s worth noting that certain providers have maintained an untarnished security record. Continuous advancement and rigorous security measures enable reputable password managers to establish a robust protective barrier.
Let’s proceed with the blog to address pivotal inquiries: How do password managers protect your passwords? What are the associated risks? And ultimately, is adopting a password manager a prudent choice?
Continue reading to delve into these essential considerations.
Password Manager
Password managers offer a secure and convenient solution for storing all your online login information in one place. With a single master password, you can access your logins effortlessly.
These apps use multiple layers of protection, making them a reliable digital security system. They can be desktop apps or cloud-based, each with its own security advantages.
A good password manager prioritizes security, employing various measures to prevent breaches and safeguard your passwords. They start with secure encryption using advanced ciphers like AES 256-bit or XChaCha20, making it virtually impossible to crack passwords within a lifetime.
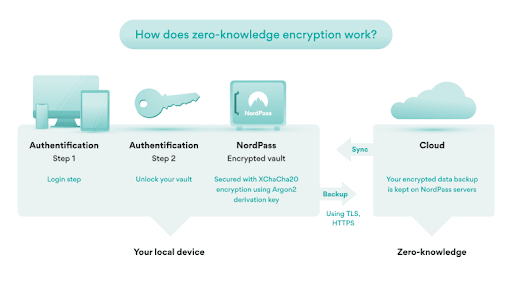
Top password managers utilize a zero-knowledge architecture, encrypting passwords on your device before they reach the server, ensuring even the provider can’t decipher them.
Some managers offer features like password strength evaluation. Many services also offer password generators for ultra-secure passwords and reminders to change them regularly.
With these features, password managers prove essential in safeguarding your data online.
Types Of Security Features In Password Managers
Password managers employ a range of robust security measures to safeguard your sensitive information. These are some of the most prevalent features:
- Encryption:
Your data is transformed into complex codes, enhancing its resistance to unauthorized access.
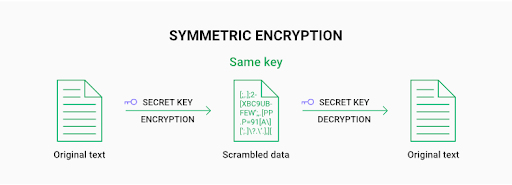
Most password managers employ AES-256 encryption, a formidable standard renowned for its toughness. Some even integrate multiple layers of encryption.
- Zero-Knowledge Architecture:
Many password managers adopt a zero-knowledge approach, ensuring that your master password, which grants access to all other passwords, remains undisclosed to the system.
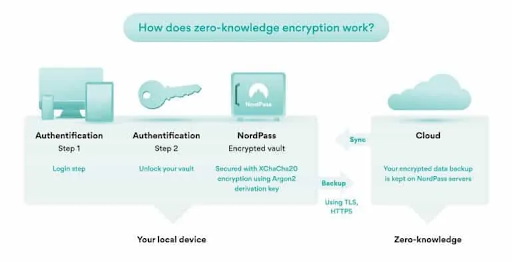
This shields your master password from potential leaks.
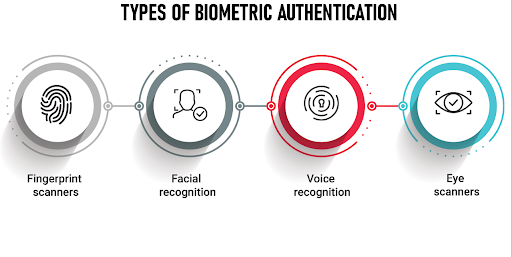
- Biometric Login:
Similar to unlocking an iPhone, numerous password managers enable users to authenticate using fingerprints or facial scans, bolstering security through biometric recognition.
- Multi Factor Authentication:
Strengthening login security, multi factor authentication mandates access from multiple devices.
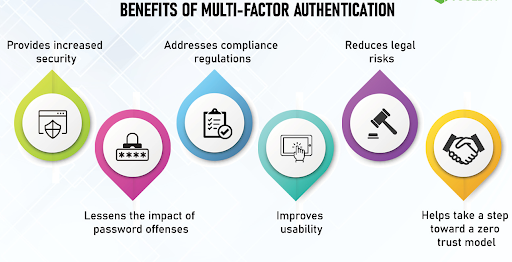
For instance, logging in on a laptop might necessitate confirmation on a linked cell phone.
- Dark Web Monitoring:
Certain password managers offer continuous monitoring of the dark web, where pilfered data may be traded.

This proactive measure detects potential breaches of your personal information.
Incorporating these security features, password managers ensure a robust defense against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Types of Password Managers: Which Is The Most Secure Type?
Password managers vary in how they store data, offering three options: cloud, browser, and local. Each method comes with distinct advantages and limitations, as well as defenses against the common types of password attacks. To better understand these options and determine the most secure one, let’s delve into each type individually.
- Browser-Based
| Pros | Cons |
| Very easy to use | No cross-browser sync |
| Free | Not all generate passwords |
While encryption and two-factor authentication offer a level of security, browser-based password managers have limitations.

They are tied to a single browser, hindering flexibility when switching. Synchronization across browsers is lacking, potentially compromising password storage.
Moreover, some lack a password generator and fail to identify weak or reused passwords. Manual creation and additional tools may be required for comprehensive security checks.
- Cloud-Based
| Pros | Cons |
| Convenient | No access to your vault security |
| Easy access from anywhere | Third-party servers store the data |
| Backup On Cloud | |
| Dependent On Internet |
Cloud-based password managers offer a crucial advantage by ensuring the backup of your vault data. This guarantees swift recovery of your database if any server-related issues arise.
Moreover, distinguished platforms such as NordPass extend beyond password storage, enabling the safekeeping of vital notes and credit card details, fortifying overall data protection.
Enhancing security further, these cloud-based solutions identify compromised and feeble passwords, proactively generate robust alternatives, and conduct regular account leak checks. Seamless sharing of vault entries, even with non-users of the same service, is an added convenience.
The versatility of cloud-based password managers is noteworthy, functioning seamlessly across various browsers and operating systems. This eliminates the need for intricate data copying and pasting methods, ensuring effortless yet secure data management.
- Desktop-Based
| Pros | Cons |
| Safe Option | No access from other devices |
| Do not require internet connection | Password sharing is complicated |
| Manual backups |
Desktop-based password managers offer potentially unparalleled safety, contingent on user actions.

These managers store data locally, confined to a single device. This offline approach minimizes online vulnerabilities, significantly reducing hacking risks. The primary threat lies in unintentional keylogger exposure, mitigated by embracing biometric authentication.
Nevertheless, this security model carries inherent drawbacks. Consistency in performing backups becomes imperative. Irreparable device failures entail potential vault loss. Mobility is restricted, barring password access from alternate devices and complicating sharing procedures.
Benefits Of Using A Password Manager
Efficiently implementing password management best practices presents challenges for most individuals. The complexities of remembering numerous strong passwords without compromising security often necessitate external aid, along with understanding the benefits and tips to choose the right one.
Embracing a password manager can significantly enhance your ability to adhere to these best practices, fostering a safer online environment.
- Generating Unique, Strong Passwords
Password managers empower users to effortlessly generate intricate, random, and robust passwords for each account. By enabling seamless copy-paste functionality during logins, these passwords can reach the highest levels of sophistication while eliminating the necessity for manual recollection.
This strategic approach also eradicates the hazardous practice of password reuse, thwarting hackers’ attempts to exploit stolen information across different accounts.
- Ensuring Reliable Backups
Cloud and browser-based password managers emerge as the most secure avenues for safeguarding password backups. Providers strategically distribute encrypted backups across multiple geographically dispersed data centers, ensuring resilience even in the face of calamity.
In contrast, self-reliant backups on paper or personal equipment lack the same level of safety and dependability. The responsibility of consistent manual backups and maintaining redundancy in diverse locations falls upon the user.
Is It Safe To Use A Password Manager?
When considering the sensitive data housed within password managers—ranging from passwords and contact details to credit card information—the question of safety naturally arises.
Let’s get into the security insights of password managers to make an informed decision:
Encryption: The Cornerstone of Protection
While instances of password manager breaches have occurred, an important distinction arises: encryption. Effective encryption, particularly utilizing industry-standard protocols like the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), serves as an impregnable barrier against malicious decryption attempts.
This renders the content virtually impenetrable to unauthorized access, reinforcing the overall security framework.
Defensive Measures within Password Managers
Password managers do not retain your master password or the encrypted contents of your database. This design choice adds an additional layer of safeguarding, minimizing exposure risks.
Emphasizing the pivotal role of your master password, its potency contributes profoundly to the security posture. Opting for a robust, meticulously guarded master password stands as a critical defensive measure.
Ultimately, while there may be some vulnerabilities, the robust encryption practices and protective mechanisms inherent in password managers provides a reassuring foundation for data security.
What Are The Risks Involved In Using A Password Manager?
While the adoption of trustworthy password managers offers enhanced online security, several potential risks warrant attention:
- Centralized Data Storage: A Double-Edged Sword
Pooling sensitive data within a password manager creates a concentrated target. The potential fallout from a breach, encompassing credit card details and secure notes, underscores the importance of swift response measures to thwart attackers, including understanding Types Of Password Attacks And How To Stop Them.
- Backup Prerequisites and Pitfalls
Dependence on server backups necessitates trust in your provider’s diligence. Opting for offline vault storage further compounds the risk, demanding meticulous precautions. Notably, reliable solutions like NordPass and Keeper alleviate this concern by maintaining backup copies in case of server disruptions.
- Device Security: A Crucial Link
The vulnerability of one device can compromise all logins. Malware-infected devices pose grave threats to password manager security, potentially capturing master passwords. A robust antivirus strategy becomes imperative to safeguarding all devices.
- Biometric Shielding: Enhanced Defense
Integrating biometric authentication, like fingerprints or face scans, erects formidable barriers against unauthorized access. Not only does it heighten security, but it also streamlines access for users across devices, exemplified by NordPass, RoboForm, and Keeper.
- Choosing Wisely: The Perils of Subpar Managers
Opting for a subpar password manager, driven by cost considerations, jeopardizes data security. Weaker encryption, limited features, and unfavorable reviews erode the protective shield, necessitating prioritization of robust options.
- Master Password Conundrum: Forgetting and Recovering
A forgotten master password, compounded by a lack of reset mechanisms, can pose a daunting challenge. Users are advised to maintain secure records or hints in physically safeguarded locations, like safes.
In assessing the panorama of password manager risks, a dual perspective emerges: certain vulnerabilities emanate from the tools themselves, while others are a product of user choices.
Excluding the latter, reputable password managers, exhibiting due diligence and safeguarding mechanisms, offer a commendable secure solution for digital credential protection.
What Should You Do if Your Passwords Are Exposed?
When confronted with compromised passwords, swift and strategic action is paramount. Adopting a proactive approach ensures containment and minimizes potential damage.
- Immediate Password Change
Upon detecting any breach, the foremost step is altering all affected passwords promptly.
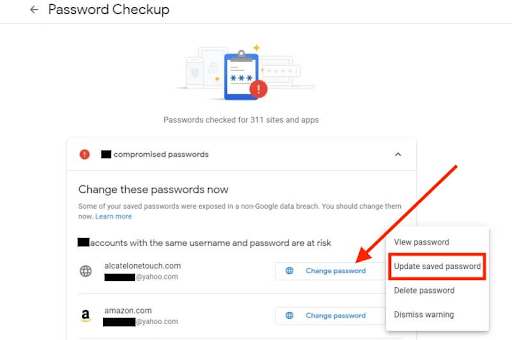
Cyberattacks often target the entities housing your accounts, rather than the fortified environment of a password manager.
- Strategic Response to Manager Credential Theft
Changing most or all passwords is advisable, coupled with the evaluation of transitioning to a different manager. If a leaked password overlaps with multiple accounts, altering all connected passwords is crucial, regardless of direct breach impact.
- Crafting Resilient New Passwords
Formulating new passwords demands precision. Incorporate a blend of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters for heightened complexity. Eschew common words to evade predictability.
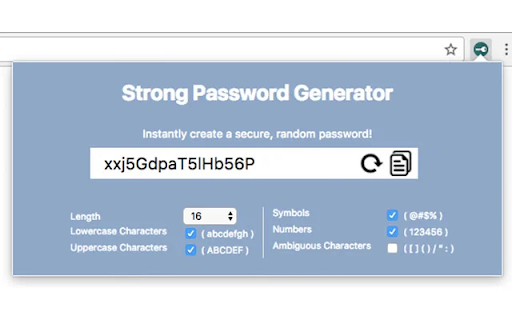
Longer passwords bolster security; many managers facilitate the creation of strong, random passwords, offering an extra layer of defense.
What If Your Password Manager Gets Hacked?
Ensuring the safety of your password manager involves acknowledging potential risks and employing vigilant countermeasures.
- Encryption Shields Your Data
Password managers operate on robust encryption, safeguarding your passwords locally.
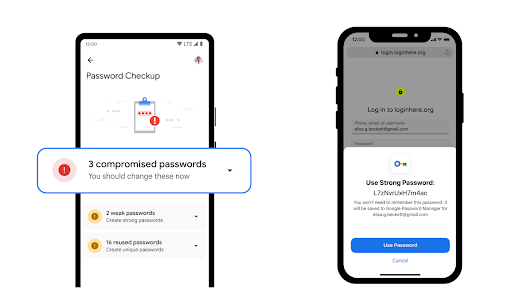
Adopting a zero-knowledge approach ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, encrypted data remains incomprehensible to hackers.
- Device-Based Vulnerabilities
Physical device breaches necessitate multifaceted infiltration, including stealing, malware, or keylogging. Yet, assailants would still require your master password.

Biometric authentication—such as fingerprints or face ID—creates an additional layer of impregnability.
- Counteracting Malware Attacks
Device contamination through malware warrants proactive responses. Reinstalling the operating system and updating passwords in the vault are prudent steps. Amplify protection by enabling 2FA or MFA, which demands supplementary authentication factors, alerting you to unusual login attempts.
- Holistic Safeguarding for Password Security
Remaining vigilant against potential threats bolsters password manager security. Encryption, biometrics, and responsive actions coalesce to preserve the sanctity of your data.
What Happens If You Forget Your Master Password?
Safeguarding access to your password manager’s master password is pivotal. Should it be lost or forgotten, exploring potential recovery avenues becomes essential, with various strategies at your disposal.
- Leveraging Recovery Codes
Certain platforms provide recovery codes during registration. Safeguard these codes diligently; they serve as a lifeline in regaining access.
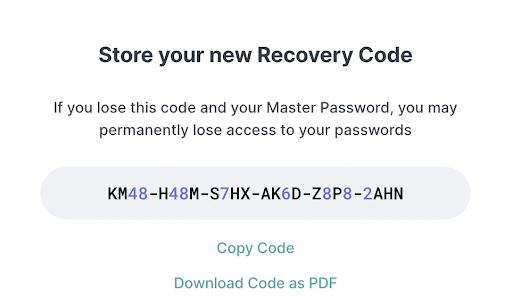
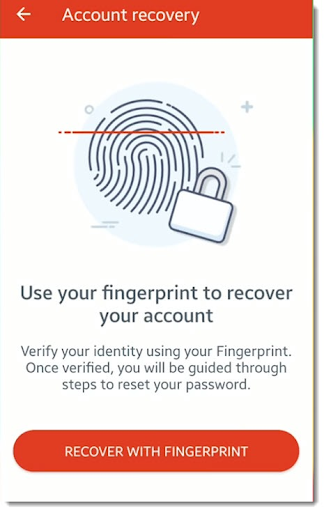
- Harnessing Biometric Security
For services incorporating biometric measures like fingerprints or face scans, a smartphone can serve as a gateway to reset the master password.
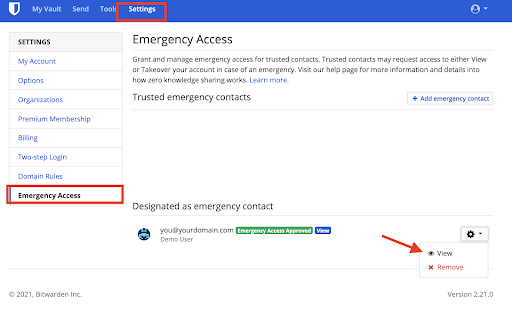
- Emergency Contact Facilitation
Some managers allow the setup of an emergency contact. If available, this contact might possess the capability to facilitate a master password reset, presenting an alternative route to account retrieval.
- Multi-Device Checkpoint
Verifying whether your manager remains logged in on another device can offer a reprieve.
Swiftly backing up your passwords before initiating an account reset or deletion preserves your data integrity.
- The Last Resort: Account Reset
In instances where recovery attempts prove futile or unavailable, an account reset becomes inevitable.
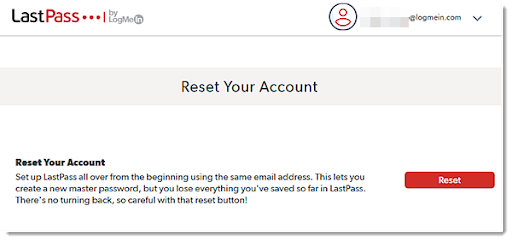
However, this course of action culminates in the loss of all saved passwords, underscoring the importance of preventative measures.